Patrick Bet-David explains how the power grid is vulnerable to attack by foreign adversaries and several other areas, and questions why power grid security is not a priority for the U.S. government.
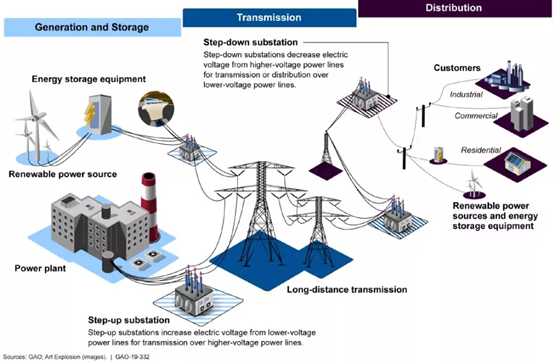
The American power grid is considered outdated and highly fragmented by energy experts, and woefully underprepared for extreme weather events. In 2021, the American Society of Civil Engineers gave the U.S. energy system a “C-“ grade on its infrastructure report card.
It added that American grid investment rates are on track to produce a $200 billion funding gap by 2029.
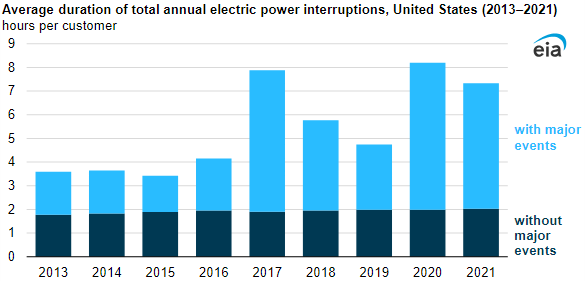
On the positive side of the things, the average experience of power outages among U.S. electricity consumers remained at around two hours per year from 2013 to 2021. We are fortunate for that fact.
Learn the benefits of becoming a Valuetainment Member and subscribe today!
On the other hand, much of the US electric grid was built in the 1960s and 1970s. Today, over 70 percent of the US electricity grid is more than 25 years old, according to the White House.
Energy systems have multiple vectors of vulnerability:
1. Extreme Weather
- Severe heat or cold
- Storms, tornadoes, hurricanes, floods
- Major power outages from weather-related events in America have increased by 67 percent since 2000.
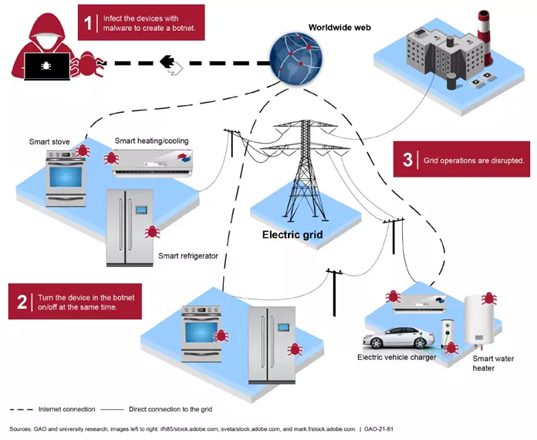
2. Cybersecurity
- In 2021, the Office of the Director of National Intelligence, which serves as the formal head of the US intelligence agencies, issued a warning in its threat assessment that Russia, China, Iran, North Korea and other adversaries have the capacity to cause harm to the US energy grid.
- US Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm echoed this evaluation.
3. EMP
- An electromagnetic pulse (EMP), also referred to as a transient electromagnetic disturbance (TED), is an event that releases a quick burst of electromagnetic energy.
- The origin of an EMP can be natural or artificial, and can occur as an electromagnetic field, an electric field, a magnetic field, or a conducted electric current.
- EMPs cause electromagnetic interference which can obstruct communications and damage electronic devices.
- There are two possible sources for an EMP: the intentional detonation of a nuclear device in the atmosphere above the earth or a gigantic solar flare. The consequences of either could range from a few days without power to life-threatening destruction.
4. Physical Attacks
- Physical attacks on power grids increased by 71 percent between 2021 and 2022.
Watch the rest of Patrick Bet-David’s video to learn more about what you can do personally to advocate for a stronger power grid.

















Add comment