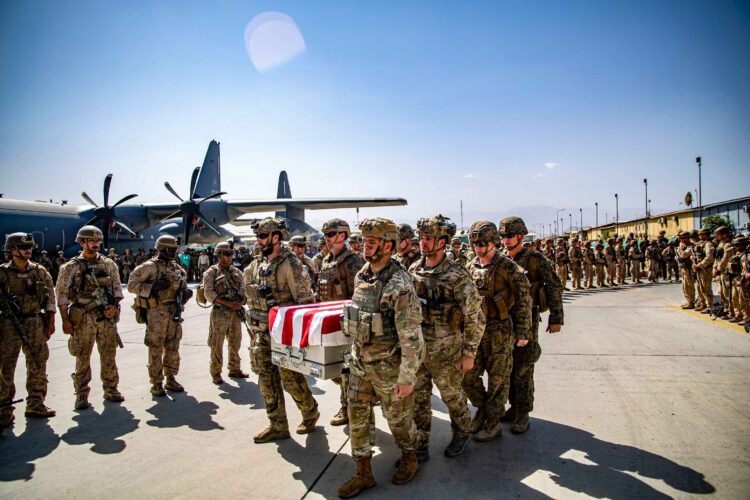
The US House of Representatives passed HR 8070 on Friday, commonly known as the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA), which included a 19.5 percent raise for junior enlisted military service members and a 4.5 percent raise for all service members.
The bill passed with 217 votes in favor and 199 against. The 211 votes in favor came from Republicans, while 196 votes against the bill came from Democrats. The 1,000+ page bill, typically passed every year, authorizes appropriations for military activities across the federal government for the following year.
The bill generally funds military operations, construction, and energy security projects, aiming to enhance the overall capabilities and resilience of the armed forces. Significant investments are allocated for advanced weaponry, cybersecurity, and critical infrastructure. The bill also addressed personnel welfare, including improved housing, healthcare benefits, and family support programs.
Learn the benefits of becoming a Valuetainment Member and subscribe today!
This year’s bill included projects related to strategic defense capabilities, labor challenges in the defense sector, supply chain security, energy and environmental security, and cybersecurity initiatives. It appropriated $1.77 billion for ballistic missile defense, a hot topic since Russian warships arrived around Cuba. The pay increases for military service members are hoped to address recruiting challenges. More than $7 billion was allocated for “Defense Environmental Cleanup,” and various cybersecurity projects received nearly $400 million. Another initiative to receive funding is $42.5 million for “energy resilience and conservation investment projects” at a “Naval Support Activity” in Souda Bay, Greece.
Overall, the 2025 Department of Defense budget has increased by one percent from the 2024 budget. While this is approximately a $8.42 billion increase, the increase does not keep pace with inflation since the passage of the 2024 budget; core inflation was 3.42 percent, measured from May 2023 to May 2024.
Many have noted the national security risk of the size of the US national debt. According to a Congressional Budget Office report in February, the US will spend $870 billion on interest for the debt in 2024—more than the budget for the Department of Defense for the year. This puts pressure on the Federal Reserve to not raise interest rates, as doing so often leads to higher interest rates on federal debt.

















Add comment